Introduction
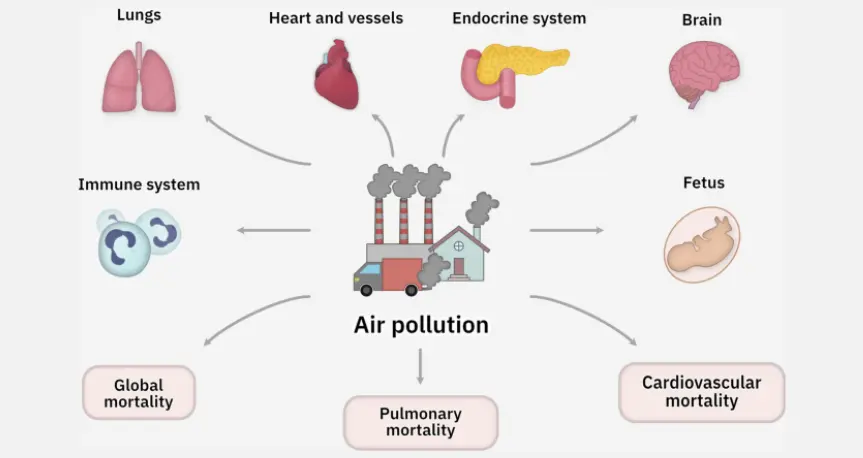
In today's modern world, air pollution has become an increasingly concerning issue, impacting not only the environment but also human health in profound ways. Among the myriad health risks associated with air pollution, one of the most alarming is its connection to heart failure. This article delves into the intricate relationship between air pollution and heart failure, shedding light on the environmental considerations that contribute to this critical health issue.
Understanding Air Pollution and Its Sources
Before delving into the impacts on heart health, it's crucial to grasp the nature of air pollution and its primary sources. Air pollution comprises a mixture of harmful particles and gases released into the atmosphere from various human activities, including industrial processes, vehicle emissions, agricultural activities, and residential heating. These pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and ozone (O3), can have detrimental effects on both the environment and human health.
The Heart of the Matter: How Air Pollution Affects Heart Health
Research has established a strong correlation between exposure to air pollution and an increased risk of heart-related ailments, including heart failure. Fine particulate matter, often referred to as PM2.5 due to its small size (2.5 micrometers or less in diameter), poses a significant threat to cardiovascular health. When inhaled, these tiny particles can penetrate deep into the lungs and enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and oxidative stress.
Moreover, nitrogen dioxide, a common air pollutant generated by combustion processes, has been linked to endothelial dysfunction, a precursor to atherosclerosis (the hardening and narrowing of arteries). This impairment of blood vessel function can elevate blood pressure and contribute to the development of heart failure over time.
Environmental Considerations: Urbanization and Population Density
Urban areas, characterized by high population density and intense vehicular traffic, often experience elevated levels of air pollution. The concentration of pollutants tends to be particularly pronounced in metropolitan regions, where industrial facilities, transportation networks, and residential areas coexist in close proximity. Consequently, individuals residing in urban environments face a heightened risk of exposure to harmful air pollutants, exacerbating their susceptibility to heart failure and other cardiovascular conditions.
Mitigating the Risks: Strategies for Cleaner Air and Healthier Hearts
Addressing the issue of air pollution requires a multifaceted approach involving government regulations, technological innovations, and public awareness campaigns. Stringent air quality standards, coupled with emissions control measures for industries and vehicles, play a crucial role in reducing pollutant levels and safeguarding public health. Additionally, promoting sustainable transportation options, such as walking, cycling, and public transit, can help alleviate traffic congestion and mitigate air pollution in urban areas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the detrimental effects of air pollution on heart health underscore the urgent need for environmental stewardship and concerted action. By addressing the root causes of air pollution and implementing effective mitigation strategies, we can protect individuals from the harmful consequences of poor air quality and pave the way for healthier, more sustainable communities. Together, let us breathe easier and strive for a future where clean air is a fundamental right enjoyed by all.







Leave a comment